 Home
Home
 Back
Back
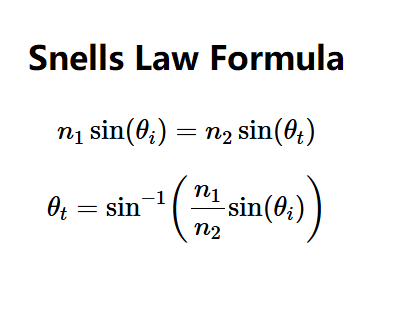
Definition: Snell's Law relates the angles of incidence and refraction (transmission) when light passes between two media with different refractive indices, allowing calculation of the angle of transmission:
Variables:
Details: Snell's Law is fundamental in optics and physics for understanding and predicting the behavior of light as it travels between different media, used in designing lenses, prisms, and optical devices.
Tips: Enter the refractive indices of the two materials and the angle of incidence with its unit (degrees or radians). Click "Calculate" to get the angle of transmission in both degrees and radians.
Q1: What is Snell's Law?
A: Snell's Law describes the relationship between the angles of incidence and refraction when light passes between two media with different refractive indices.
Q2: What is the refractive index?
A: The refractive index (\( n \)) is a dimensionless number that describes how much light slows down and bends in a medium compared to a vacuum.
Q3: What is the angle of transmission?
A: The angle of transmission (\( \theta_t \)) is the angle between the refracted light ray and the normal (perpendicular) to the surface at the point of refraction.
Q4: What is total internal reflection?
A: Total internal reflection occurs when the angle of incidence exceeds the critical angle, causing the light to reflect entirely within the first medium (when \( \sin(\theta_t) > 1 \)).
Q5: How accurate is this calculator?
A: The calculator is accurate based on Snell's Law and the input values, assuming ideal conditions. Real-world factors like dispersion or surface imperfections may introduce variations.