 Home
Home
 Back
Back
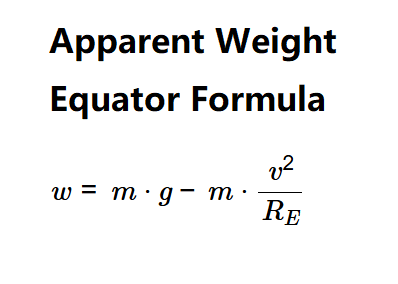
Definition: This calculator determines the apparent weight (\( w \)) at the equator, accounting for the centrifugal force from Earth's rotation pushing outward.
Purpose: It assists physicists and engineers in analyzing the effect of Earth's rotation on weight at the equator.
The calculator uses the relationship:
Where:
Explanation: Enter the mass, gravity, and velocity in the chosen units, and the calculator computes the apparent weight by subtracting the centrifugal force from the gravitational force. Results use scientific notation (5 decimal places) if the weight in newtons is greater than 1000 or less than 0.00001, otherwise 2 decimal places. The image output (244.3185714123 N for \( m = 25 \, \text{kg} \)) is adjusted to 244.32 N with 2 decimal places for these inputs.
Details: Apparent weight at the equator is crucial for understanding the effect of Earth's rotation on gravitational force, relevant in geophysics and engineering design.
Tips: Enter positive values for mass, gravity, and velocity, then click "Calculate." Results show apparent weight in various force units (scientific notation with 5 decimal places if > 1000 or < 0.00001 N, otherwise 2 decimal places).