 Home
Home
 Back
Back
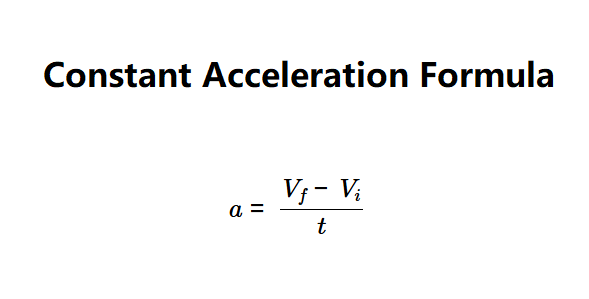
Definition: This calculator determines the constant acceleration (\( a \)) of an object, based on its initial velocity (\( V_i \)), final velocity (\( V_f \)), and time (\( t \)).
Purpose: It assists in understanding the rate of change of velocity over time, useful in physics, engineering, and automotive applications such as motion analysis and vehicle performance.
The calculator uses the relationship:
Where:
Explanation: Enter the initial velocity, final velocity, and time in the chosen units, and the calculator computes the acceleration. Results use scientific notation (5 decimal places) if the acceleration in m/s² is greater than 10000 or less than 0.00001, otherwise 2 decimal places. For default inputs (\( V_i = 5 \, \text{m/s} \), \( V_f = 15 \, \text{m/s} \), \( t = 2 \, \text{s} \)), the calculated acceleration is 5 m/s².
Details: Acceleration measures the rate of change of velocity, indicating how quickly an object’s speed or direction changes. It’s essential for analyzing motion in vehicles, machinery, and projectile trajectories.
Tips: Enter positive or negative values for initial and final velocities (depending on direction), a positive value for time, and ensure \( t \neq 0 \), then click "Calculate." Results show the acceleration in meters/second², feet/second², and g (scientific notation with 5 decimal places if > 10000 or < 0.00001 m/s², otherwise 2 decimal places).