 Home
Home
 Back
Back
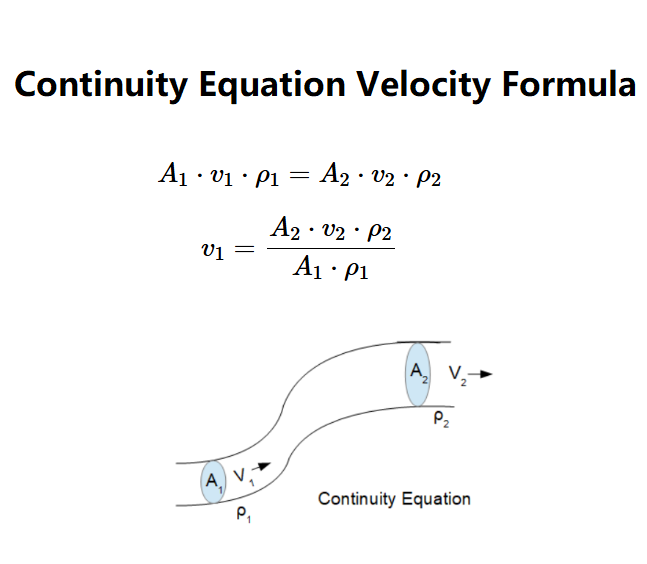
Definition: The continuity equation expresses the conservation of mass for a fluid flowing through a pipe or channel, allowing calculation of velocity at one section, using the formula:
Variables:
Details: The continuity equation is fundamental in fluid dynamics to analyze and design systems involving fluid flow, such as pipes, ducts, and nozzles, ensuring mass conservation.
Tips: Enter the areas at sections 1 and 2, velocity at section 2, and densities at sections 1 and 2 with their respective units. Click "Calculate" to get the velocity at section 1 in multiple units.
Q1: What is the continuity equation?
A: It is a mathematical statement of the conservation of mass for fluids, stating that the mass flow rate is constant through a system.
Q2: What does area represent in this context?
A: Area refers to the cross-sectional area of the flow path at different sections (e.g., pipes or ducts).
Q3: Why calculate velocity using the continuity equation?
A: It helps determine the velocity at one section of a flow when area or density changes, critical for fluid system design.
Q4: Can I use different units?
A: Yes, the calculator supports area units (m², cm², in², ft², yd²), velocity units (m/s, ft/s, km/h, mph), and density units (kg/m³, g/cm³, lb/ft³).
Q5: How accurate is this calculator?
A: The calculator is accurate based on the formula and input values, assuming steady flow. Real-world factors like turbulence may introduce variations.