 Home
Home
 Back
Back
Definition: This calculator computes the drag force (\( F_{\text{Drag}} \)) on an object moving through a fluid, based on the drag coefficient (\( C_{\text{Drag}} \)), flow velocity (\( V \)), body surface area (\( A \)), and fluid density (\( \rho \)).
Purpose: It is used in aerodynamics and fluid dynamics to analyze the resistance experienced by objects (e.g., vehicles, aircraft, or projectiles) moving through air or water, aiding in design and performance optimization.
The calculator uses the relationship:
Where:
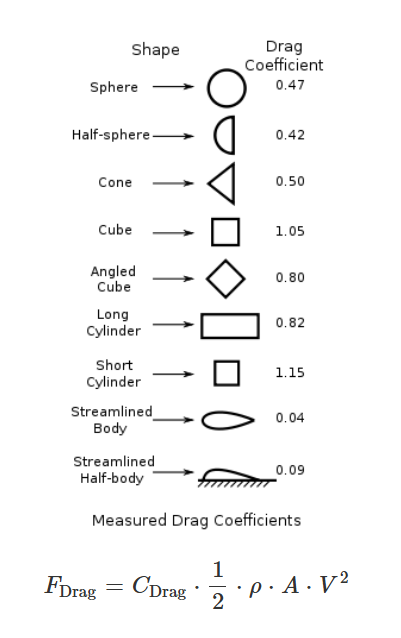
Explanation: Enter the drag coefficient, flow velocity, body surface area, and fluid density in the chosen units, and the calculator computes the drag force. Results are displayed with 5 decimal places. For default inputs (\( C_{\text{Drag}} = 0.47 \) (sphere), \( V = 10 \, \text{m/s} \), \( A = 0.5 \, \text{m}^2 \), \( \rho = 1.225 \, \text{kg/m}^3 \) (air at sea level)), the calculated drag force \( F_{\text{Drag}} \) is approximately 14.39375 N.
Details: Drag force is a critical factor in designing vehicles, aircraft, and structures exposed to fluid flow. Understanding drag helps optimize shapes for reduced resistance, improving fuel efficiency and performance.
Tips: Enter positive values for drag coefficient, velocity, area, and density with up to 4 decimal places (step of 0.0001), then click "Calculate." Results show the drag force \( F_{\text{Drag}} \) in Newtons, pounds-force, and dynes, always with 5 decimal places. Typical drag coefficients include: Sphere (0.47), Half-sphere (0.42), Cone (0.50), Cube (1.05), Long Cylinder (0.82), Short Cylinder (1.15), Streamlined Body (0.04).