 Home
Home
 Back
Back
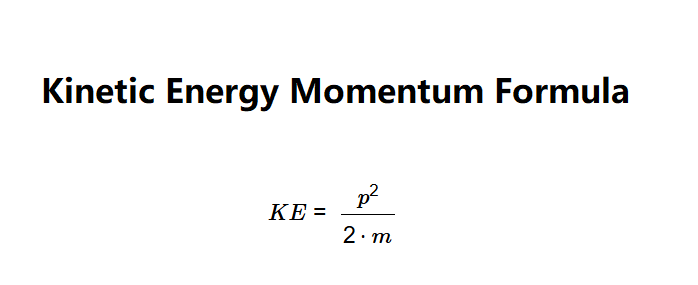
Definition: This calculator computes the kinetic energy (\( KE \)) of an object based on its momentum (\( p \)) and mass (\( m \)).
Purpose: It is used in classical mechanics to determine the energy associated with an object’s motion when momentum is known, applicable in physics problems involving collisions and dynamics.
The calculator uses the relationship:
Where:
Explanation: Enter the mass and momentum in the chosen units, and the calculator computes the kinetic energy. Results are displayed with 5 decimal places, using scientific notation if the value exceeds 100,000 or is less than 0.0001. For default inputs (\( m = 2 \, \text{kg} \), \( p = 10 \, \text{kg·m/s} \)), the calculated kinetic energy \( KE \) is 25.00000 joules.
Details: Calculating kinetic energy using momentum is useful in scenarios where momentum is directly measured or conserved, such as in collision analysis, aiding in the understanding of energy transfer in physical systems.
How do I find the kinetic energy using momentum?
Measure the momentum in kg·m/s and the mass in kilograms. Compute the kinetic energy using the formula \( KE = \frac{p^2}{2 \cdot m} \). The result will be in joules.
How can I find momentum with kinetic energy and mass?
Measure the kinetic energy in joules and the mass in kilograms. Use the equation \( KE = \frac{p^2}{2 \cdot m} \) and solve for \( p \): \( p = \sqrt{2 \cdot m \cdot KE} \), ensuring \( m \neq 0 \).
What is the formula for kinetic energy using momentum?
The formula for kinetic energy using momentum is \( KE = \frac{p^2}{2 \cdot m} \), where \( p \) is the momentum and \( m \) is the mass. The standard unit for kinetic energy is joules (J).