 Home
Home
 Back
Back
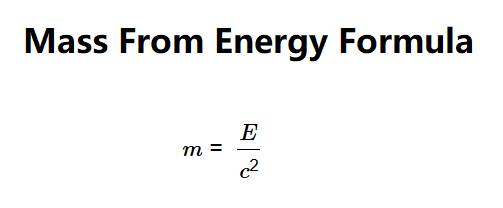
Definition: This calculator computes the mass (\( m \)) equivalent of a given energy (\( E \)) using Einstein's mass-energy equivalence principle.
Purpose: It is used in physics to determine the mass of a particle or object based on its energy, applicable in particle physics and relativity studies.
The calculator uses the relationship:
Where:
Explanation: Enter the energy in the chosen unit (joules, TWh, feV, neV, µeV, meV, eV, keV, MeV, or peV), and the calculator computes the equivalent mass. Results are displayed with 5 decimal places, using scientific notation if the value exceeds 100,000 or is less than 0.0001. For a default energy of \( E = 1 \, \text{MeV} \), the calculated mass \( m \) is approximately \( 1.78266 \times 10^{-30} \, \text{kg} \).
Details: Calculating mass from energy is fundamental in understanding mass-energy equivalence, aiding in particle physics experiments, nuclear reactions, and theoretical studies in relativity.
How do I find the mass from energy?
Measure the energy in your chosen unit, convert it to joules if necessary, and compute the mass using the formula \( m = \frac{E}{c^2} \), where \( c = 299,792,458 \, \text{m/s} \). The result will be in kilograms.
What does mass-energy equivalence mean?
Mass-energy equivalence, described by Einstein's equation \( E = mc^2 \), means that mass and energy are interchangeable; a certain amount of energy can be converted into mass, and vice versa.
What is the formula for mass from energy?
The formula for mass from energy is \( m = \frac{E}{c^2} \), where \( E \) is the energy, and \( c \) is the speed of light. The standard unit for mass is kilograms (kg).