 Home
Home
 Back
Back
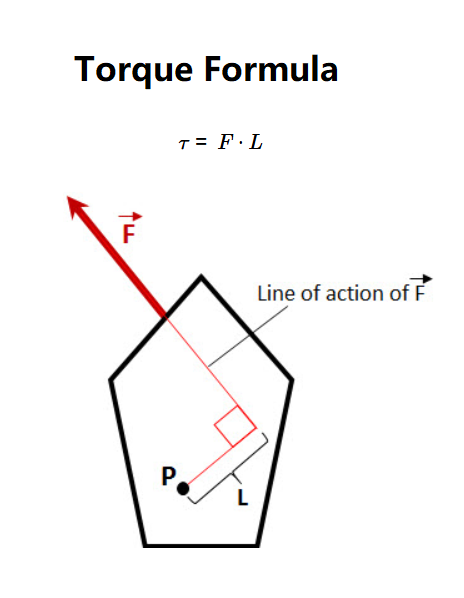
Definition: This calculator computes the torque (\( \tau \)) generated by a force (\( F \)) applied perpendicular to a distance (\( L \)) from the pivot point.
Purpose: It is used in physics and engineering to determine the rotational force or moment, applicable in mechanics, machinery design, and structural analysis.
The calculator uses the relationship:
Where:
Explanation: Enter the force and perpendicular distance in the chosen units, and the calculator computes the torque. Results are displayed with 5 decimal places, using scientific notation if the value exceeds 100,000 or is less than 0.0001. For default inputs (\( F = 10 \, \text{N} \), \( L = 1 \, \text{m} \)), the calculated torque \( \tau \) is 10.00000 N·m.
Details: Calculating torque is essential for understanding rotational motion and equilibrium, aiding in the design of engines, tools, and structural systems.
How do I find the torque?
Measure the force in newtons and the perpendicular distance in meters. Compute the torque using the formula \( \tau = F \cdot L \). The result will be in newton-meters.
What does torque represent?
Torque represents the rotational equivalent of linear force, measuring the tendency of a force to rotate an object about an axis.
What is the formula for torque?
The formula for torque is \( \tau = F \cdot L \), where \( F \) is the force, and \( L \) is the perpendicular distance to the line of force. The standard unit for torque is newton-meters (N·m).