 Home
Home
 Back
Back
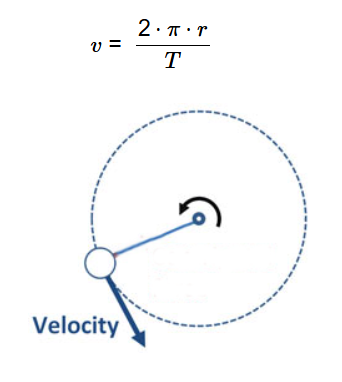
Definition: This calculator computes the velocity (\( v \)) of an object in orbit based on the radius of the orbit (\( r \)) and the orbital period (\( T \)).
Purpose: It is used in astronomy and physics to determine the speed of an object in a circular orbit, applicable in planetary motion, satellite dynamics, and space missions.
The calculator uses the relationship:
Where:
Explanation: Enter the radius and period in the chosen units, and the calculator computes the orbital velocity. Results are displayed with 5 decimal places, using scientific notation if the value exceeds 100,000 or is less than 0.0001. For default inputs (\( r = 1 \, \text{au} \), \( T = 1 \, \text{year} \)), which approximates Earth’s orbit around the Sun, the calculated velocity \( v \) is approximately 29.78592 m/s.
Details: Calculating the velocity in orbit is essential for understanding the motion of celestial bodies and satellites, aiding in the design of space missions, orbital trajectories, and satellite systems.
How do I find the velocity of an object in orbit?
Measure the radius of the orbit in meters and the orbital period in seconds. Compute the velocity using the formula \( v = \frac{2 \cdot \pi \cdot r}{T} \). The result will be in meters/second.
What does velocity in orbit represent?
Velocity in orbit represents the tangential speed of an object moving in a circular path around a central body, such as a planet orbiting a star or a satellite orbiting a planet.
What is the formula for velocity in orbit?
The formula for velocity in orbit is \( v = \frac{2 \cdot \pi \cdot r}{T} \), where \( r \) is the radius of the orbit, and \( T \) is the orbital period. The standard unit for velocity is meters/second (m/s).